In the realm of pediatric orthopedics, addressing knee deformities in children demands a nuanced approach that combines expertise, empathy, and cutting-edge medical knowledge. At Child ortho spin care, we understand the intricate nature of pediatric knee conditions and are committed to providing unparalleled care. This comprehensive guide sheds light on the diagnosis and treatment of knee deformities in children, offering valuable insights for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Understanding Pediatric Knee Deformities
Identifying Early Signs
Recognizing the early signs of knee deformities is crucial for prompt intervention. Children may exhibit symptoms such as gait abnormalities, joint stiffness, or persistent pain. Observant parents and vigilant healthcare providers play a pivotal role in early detection, ensuring a proactive response to potential issues.
Common Types of Pediatric Knee Deformities
- Genu Varum (Bowlegs):
- Description: Genu varum is characterized by an outward bowing of the legs. Our expert pediatric orthopedists employ advanced imaging techniques to assess the severity and formulate personalized treatment plans.
- Treatment Options: From bracing to surgical interventions, our team tailors approaches to the unique needs of each child.
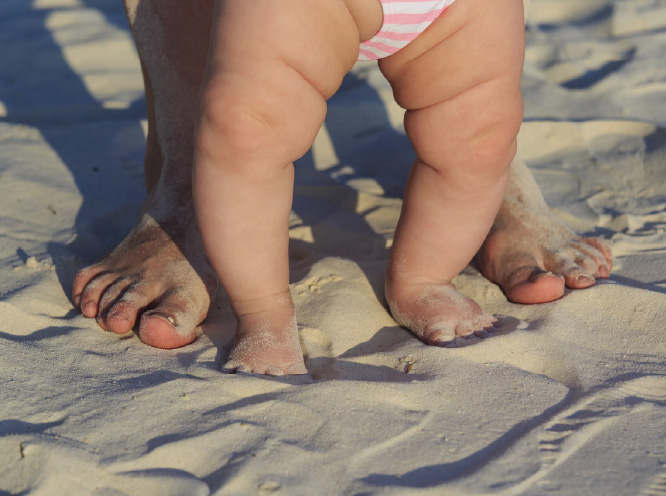
- Genu Valgum (Knock-Knees):
- Description: Genu valgum involves an inward angulation of the knees. Timely identification is crucial to prevent potential complications in gait and joint health.
- Treatment Approaches: Non-surgical interventions, including physical therapy, are often effective in mild cases, while severe conditions may necessitate surgical correction.
Diagnostic Process
Our commitment to precision begins with a meticulous diagnostic process.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Accurate diagnosis is facilitated by state-of-the-art imaging technologies, including:

Treatment Modalities
Non-surgical Approaches
- Orthotic Devices:
- Customized orthotic devices are designed to provide support and correct deformities, fostering natural limb development.
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises and physical therapy regimens are integral in mild to moderate cases, promoting musculoskeletal balance.
Surgical Interventions
- Epiphysiodesis:
- In cases where growth plate abnormalities contribute to deformities, epiphysiodesis is a surgical technique to modulate growth patterns.
- Osteotomy:
- Precision surgeries like osteotomy aim to realign bones, correcting deformities and restoring optimal function.
Post-Treatment Care and Rehabilitation
Collaborative Approach
Our commitment extends beyond surgical interventions, emphasizing collaborative post-treatment care:
- Rehabilitation Programs:
- Tailored rehabilitation programs ensure a seamless transition from surgery to restored mobility.
- Long-term Follow-up:
- Regular follow-ups track progress, addressing any emerging concerns and fostering a supportive continuum of care.
Conclusion
At Child ortho spin care, our dedication to excellence in pediatric orthopedics is unwavering. This guide serves as a testament to our commitment to empowering parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals with comprehensive insights into the intricate domain of pediatric knee deformities. For personalized consultations and unparalleled care, trust Child ortho spin care to lead the way in pediatric orthopedic excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Pediatric Knee Deformities
Q1: What are the early signs of knee deformities in children?
A1: Early signs may include gait abnormalities, joint stiffness, and persistent pain. Vigilant parents and healthcare providers play a crucial role in early detection.
Q2: What types of knee deformities are common in children?
A2: Common types include Genu Varum (Bowlegs) and Genu Valgum (Knock-Knees). Timely identification is vital to tailor appropriate interventions.
Q3: How are knee deformities diagnosed?
A3: Our diagnostic process involves advanced imaging techniques, including X-rays, MRI, and CT scans. Digital imaging analysis ensures precise diagnosis and personalized treatment planning.
Q4: What non-surgical treatments are available?
A4: Non-surgical approaches include customized orthotic devices for support and physical therapy to promote musculoskeletal balance.
Q5: When is surgery recommended for pediatric knee deformities?
A5: Surgery may be recommended for severe cases. Surgical interventions such as epiphysiodesis and osteotomy aim to correct deformities and restore optimal function.

